What is Computer Numerical Control (CNC)?
Key Essentials for Understanding
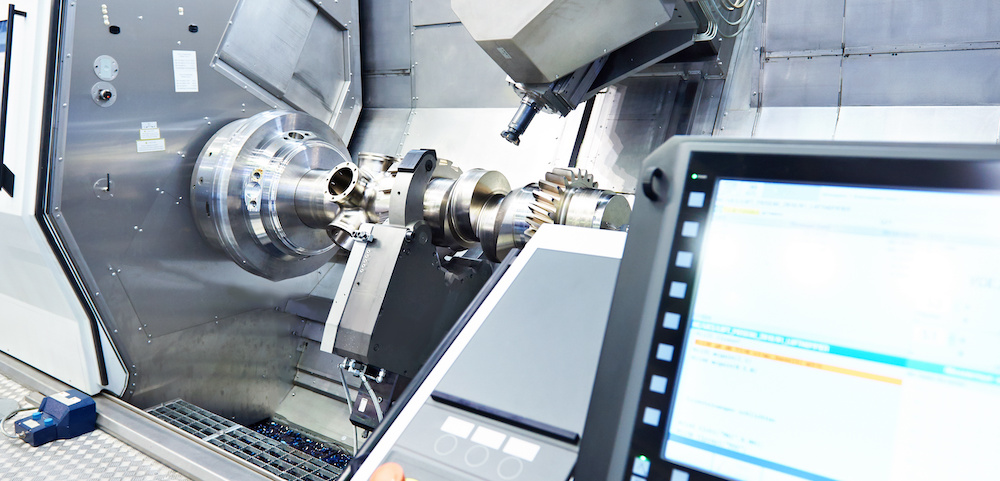

With advancements in IT technology, the manufacturing industry is increasingly focusing on IT integration and automation to improve efficiency. One of the key methods for automating machining processes is computer numerical control (CNC). Machines equipped with CNC are referred to as “CNC machines” and utilized in the production of industrial parts. The benefits of CNC include the ability to mass-produce products with consistent quality and high safety standards. This article will provide an overview of CNC, its applications, advantages and disadvantages, and the types of machining it can perform.
Table of Contents
What is CNC?
Computer numerical control (CNC) means using a computer to control machines numerically. By automating machine movements (such as direction, speed, and cutting amount) through programming, high-quality products can be produced safely and efficiently.
In the past, the operation of machines such as milling machines and lathes was performed entirely by skilled craftsmen. However, this method led to issues such as variations in output due to the craftsman’s skill level, an inability to process complex shapes, and inefficiencies in work processes. By automating the movements of machines through numerical control, these problems can be resolved. Today, many machines are equipped with the technology. Furthermore, by combining CNC machines with computer-aided design (CAD) and computer-aided manufacturing (CAM), the entire process from design to machining can be completed with a computer.
Applications of CNC Machines
Machines operating under numerical control are used in various applications, including manufacturing parts for automobiles, medical devices, and aircraft, as well as machining molds. They are particularly useful for performing precise operations, such as freeform machining and three-dimensional shape processing, which are difficult with conventional (non-numerical) manual machines. Additionally, some CNC machines can process plastics and wood as well as metals.
Differences Between CNC and NC
A similar term to CNC is numerical control (NC). The main difference is that NC does not include the word “computer.”
NC refers to the method of controlling machine operations using only hardware like transistors and arithmetic circuits. Developed in the 1950s, it typically involved combining multiple circuit boards for data reading, calculations, and servo control. In contrast, CNC replaces the NC control mechanism with a computer (microcontroller). It controls machine operations through specialized programming languages. However, in recent years, many NC devices have also started to incorporate computers, blurring the distinction between NC and CNC.
How to Use CNC
When processing materials with CNC, the process generally follows these steps:
2. Generate NC program data using CAM.
3. Prepare the necessary tools and secure them in the tool holder.
4. Set the material on the machining platform.
5. Start the machining process.
While CAD is a tool for creating 3D data, CAM is an application that generates NC programs based on 3D data created in CAD. NC programs detail the tool’s rotation speed, type, timing for tool changes, and the tool’s path. By inputting tools and machining conditions into CAM, NC programs can be generated automatically, allowing CNC machining without needing programming knowledge.
Features of CNC
Advantages
・Stable Quality
When craftsmen manually operate machines, there can be variations in product quality. For instance, differences in size and condition can occur based on the craftsman’s skill level, and operational mistakes may lead to waste. CNC machines perform machining automatically based on programmed instructions, helping to maintain relatively consistent product quality.
・Suitable for Mass Production and Cost Reduction
The machines operate with numerical control, minimizing unnecessary movements and typically completing machining faster than manual labor. The shorter machining time per piece allows for efficient mass production of the same product. Additionally, during machine operation, the operator only needs to monitor the machine, allowing one person to oversee multiple machines. In some cases, the machines can even operate completely unmanned. This enables a small number of personnel to produce a large volume of products, enhancing productivity and reducing labor costs.
・High Safety
CNC machines can operate automatically without the need for an operator to be nearby. This significantly reduces the risk of injury from machine entanglement or flying debris. However, using improperly sized workpieces (such as long rods that extend beyond the machine) can still pose serious injury risks, so it is essential to verify the machine’s operational parameters before proceeding.
・Automation of Tool Changes with ATC
An automatic tool changer (ATC) is a device that automatically changes tools during CNC machining. Following NC programming, it automatically swaps out preset tools such as mills and drills for continuous machining. When combined with such devices, there’s no need to stop the machine for manual tool changes or to use separate machines for different processes, resulting in efficient machining with reduced downtime.
Disadvantages
・High Equipment Costs
CNC machines incorporate computers and software for numerical control alongside the actual machining components. As a result, they are significantly more expensive than conventional machines, leading to high initial investment costs. Additionally, in some cases, a separate CAM system may need to be purchased. It is essential to assess the potential for recouping these costs before proceeding with acquisition.
・Extensive Preparation Before Machining
Automating machining processes with CNC requires extensive preparation, including learning to program NC, creating and inputting NC programs, positioning materials, and conducting test cuts. The increased number of preparation steps compared to those required for conventional machines can lead to longer setup times before the first part is machined. It is therefore important to consider both the efficiency gains from automation and the time needed for preparation when estimating total work time.
Types of Machining Possible with CNC
There are various types of CNC machines available today. Once started, these machines will continue to operate automatically according to their programs. This allows for machining even during off-hours when craftsmen are not present, improving utilization and productivity. Additionally, CNC machines can achieve high precision in complex three-dimensional shapes. Below are some representative types:
Milling Machine
A CNC milling machine is a milling machine equipped with CNC functions. It automates milling processes, where a rotating cutting tool is applied to a fixed workpiece.
Lathe
A CNC lathe automates lathe machining, where a rotating workpiece is cut by a fixed tool. It can automatically process stepped shafts, and machines capable of working to 0.001 mm precision also exist.
Grinding Machine
Used for grinding processes, a CNC grinding machine applies a high-speed rotating grinding wheel to the workpiece. It can automatically change grinding wheels and control the grinding range.
Machining Center
A machining center is also a type of CNC machine. They can continuously perform multiple types of machining (such as boring, milling, drilling, tapping, and reaming), and they vary in size, shape, and the number of axes they can move.
Other Machines
CNC laser cutting machines, which use light energy to melt workpieces, and CNC waterjet cutting machines, which use high-pressure water jets to cut materials, are also types of CNC machines.
Conclusion
CNC automates the operation of machines using computers. By programming the movement direction, speed, and cutting amount, it enables high-precision numerical control. Machines equipped with CNC functions are referred to as CNC machines and used across various fields of manufacturing, including for automotive and medical devices.
CNC machines allow for mass production of consistently high-quality products. In addition, since operators are not required to be present, the risk of injury and accidents is reduced. However, the high cost of equipment and the extensive preparation required are notable disadvantages.
The machines play a significant role in enhancing operational efficiency and safety. It is important to consider both the advantages and disadvantages when determining how to effectively integrate them with conventional machines.
What’s meviy?
On-demand, fast sourcing of quality custom mechanical parts is made possible by meviy.
meviy is one of the most reliable on-demand manufacturing platforms in the US that allows you to get instant quotes for your mechanical parts simply by uploading 3D CAD data. No longer need to create 2D drawings just to quote parts. This platform supports sheet metal fabrication and CNC machining such as milling or turning and has saved time for over 160,000 mechanical designers and purchasers worldwide.