What is Electroless Nickel Plating?

Electroless nickel plating is a unique surface finish created through a chemical reaction, without the use of electricity. Its characteristics can vary, and it is increasingly used across industries such as automotive, precision machinery, electronics, and food processing. In this article, we’ll cover the differences in these characteristics, recommend suitable applications, and explain the processing steps.
Table of Contents
Features of Electroless Nickel Plating
- Provides electrical resistance, corrosion resistance, and solderability
- Coating is hard and resistant to scratches
- Coating thickness is uniform, allowing for high dimensional accuracy
Effect of Phosphate Content on Properties
Electroless nickel plating can be classified into three types based on the phosphorus content of the coating. The characteristics vary with phosphorus content, allowing for different applications based on specific needs.
The differences in characteristics are summarized in the table, illustrating the characteristics and applications of electroless nickel plating based on phosphorus content. Each symbol in the table indicates the results of comparisons based on phosphorus content.
| Phosphorus Content
(Reference) |
Low (1–4 wt%) |
Medium (5–10 wt%) |
High (11–14 wt%) |
|||
| Electrical Resistance | △ | 〇 | ◎ | |||
| Wear Resistance | ◎ | 〇 | 〇 | |||
| Corrosion Resistance | △ | 〇 | ◎ | |||
| Magnetism | 〇 | △ | × | |||
| Solderability | 〇 | △ | × | |||
| Recommended Applications | Wear Resistance: Valve components Solderability: Printed circuit boards |
Electrical Resistance: Electronic components, computer cases, areas prone to static electricity |
Magnetism: Underlayers for hard disks, areas where heat generation is expected* |
|||
• Corrosion Resistance: The ability to resist rust and corrosion.
• Electrical Resistance: How resistant a material is to the flow of electric current.
• Magnetism: The strength of a material’s magnetic properties.
• Wear Resistance: The ability to withstand wear and tear.
• Solderability: How easily a material can be soldered.
Plating Steps and Factors Affecting Features
Why does phosphorus content affect the characteristics? The electroless nickel plating process involves several key factors, which we will explain in the following steps. The process typically includes six main stages. The phosphorus content of the coating is influenced by the type of treatment solution and the temperature conditions in the plating bath during the “Plating” stage.
Electroless Nickel Plating Processing Steps:
| 1. Degreasing: Remove oils, dirt, and debris from the workpiece that can cause unevenness, preparing it for surface treatment. |
| 2. Cleaning: Wash away chemicals used during degreasing. |
| 3. Acid Cleaning: Use an acidic solvent to remove contaminants and oxides, creating a surface texture that helps the plating adhere better. |
| 4. Plating: Immerse the workpiece in a solution to form the coating. The phosphorus content of the coating varies with the treatment solution and conditions, affecting the characteristics. |
| 5. Cleaning: Rinse off the plating solution to clean the surface. |
| 6. Drying: Remove moisture from cleaning to prevent water spots and other marks on the surface. |
Factors Affecting Electrical Resistance and Magnetism
So, why do the characteristics of the coating, such as electrical resistance and magnetism, change with different phosphorus levels? We will focus on these aspects and explain the reasons behind these changes.
The factors affecting changes in electrical resistance and magnetism are related to the “coating structure.” When there is a high phosphorus content, phosphorus acts as an impurity, preventing crystallization and resulting in an “amorphous” coating structure. On the other hand, with low phosphorus content, crystallization occurs, leading to a “crystalline” coating structure.
In the “amorphous” state (see Figure 1), as indicated by the arrows, electrons and magnetic forces do not flow smoothly, resulting in higher electrical resistance and non-magnetic properties. Conversely, in the “crystalline” state (see Figure 2), electrons and magnetic forces flow more smoothly.
The examples below illustrate how phosphorus content can alter the characteristics of the same “electroless nickel plating.”
Diagram of Coating Structure
Red arrows indicate the flow of electrons and magnetic forces.
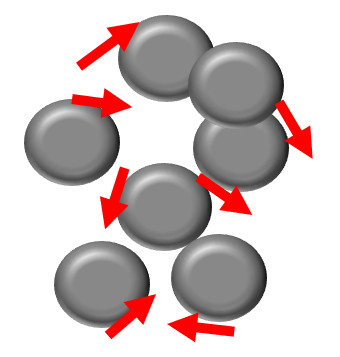
Figure 1. High Phosphorus Content
• Results in an “amorphous” state.
• Electrons and magnetic forces flow scatteredly.-
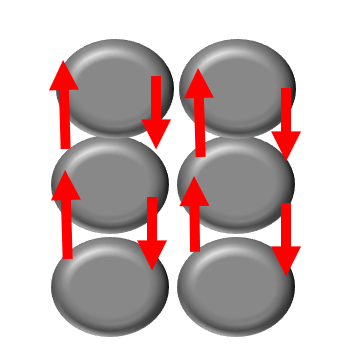 Figure 2. Low Phosphorus Content
Figure 2. Low Phosphorus Content• Results in a “crystalline” state.
• Electrons and magnetic forces flow smoothly.
Conclusion
Electroless nickel plating is a versatile and effective surface finishing process used across various industries. The properties of the coating, such as electrical resistance, wear resistance, corrosion resistance, and solderability, are heavily influenced by the phosphorus content, allowing manufacturers to customize the plating for specific applications like electronic components, wear-resistant parts, or corrosion-prone environments. By understanding the relationship between phosphorus levels and coating structure, manufacturers can optimize performance and durability, making electroless nickel plating an ideal solution for a wide range of needs.
meviy Sheet Metal, CNC Milling and Turning
Surface Finishes Option
meviy offers custom parts manufactured through CNC milling, turning, and sheet metal fabrication, with a wide range of surface finishes, starting with electroless nickel plating.
-
CNC Milling
・Electroless Nickel Plating
・Black Oxide
・Trivalent Chromate (Clear/ Black)
・Anodizing
(Clear/ Black/ Matte Black/ Red/ Gold)
・Hard Anodize (Clear)
・Hard Chrome Plating (Flash Plating)
・Low Temperature Black Chrome
・Phosphate Coating
-
CNC Turning
・Electroless Nickel Plating
・Black Oxide
・Trivalent Chromate (Clear/ Black)
・Anodizing (Clear/ Black/ Matte Black)
・Hard Anodize (Clear)
・Salt-Bath Nitrocarburizing
・Low Temperature Black Chrome
・Phosphate Coating -
Sheet Metal
・Electroless Nickel Plating
・Black Oxide
・Trivalent Chromate (Clear/ Black)
・Anodizing (Clear/ Black/ Matte Black)
・Painting (Power Coating/ Wet Paint) 
meviy Sheet Metal
Sample Parts with Electroless Nickel Plating
Cover
Materials
1018 Steel Size
(W x D x H) (mm)100 × 135 × 80 Days to Ship
(as soon as)7 days 
Bracket
Materials 1018 Steel Size
(W x D x H) (mm)
55 × 95 × 150 Days to Ship
(as soon as)7 days 
Base Plate
Materials 1018 Steel Size
(W x D x H) (mm)
100 × 130 × 12.4 Days to Ship
(as soon as)7 days






