- HELP
- Technical Information
- Welded Sheet Metal
- Applicable Parts/Materials
- Instructions and Details for Welding Information
Instructions and Details for Welding Information
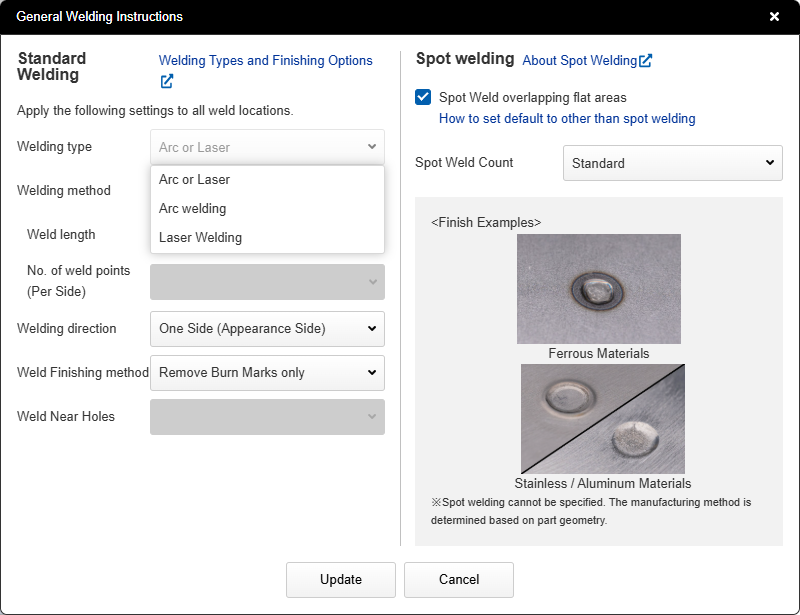
- In the [Welding Information] menu, you can set the weld type, welding method, welding direction, and finishing method.
- Welding information applies to all weld locations.
- *For how to set welding information indicators, see “Setting Welding Information“.
Welding Type
- Select from Standard (Arc or Laser), Arc Welding, or Laser Welding.
- For products with overlapping weld sections, Spot Welding can also be selected.
 |
|

Arc welding |

Laser Welding |

Spot Welding |
|
Standard (Arc or Laser)
- We manufacture and ship using either arc welding or laser welding.
- The welding type during production is determined based on the conditions specified in your request, such as material, plate thickness, and product shape.
Arc Welding
- This process joins the contact points of components using the arc discharge phenomenon. Types include TIG welding and Semi-Automatic welding.
- Arc welding is widely used and offers the advantages of low-cost fabrication and a wide weld bead width.
- While distortion can occur due to heat effects during welding, this can be mitigated by methods such as intermittent welding to shorten the weld length.
Laser Welding
- This process joins the contact points of components by utilizing the melting effect of laser light irradiation. It includes fiber laser welding and YAG laser welding.
- It features a narrow weld bead width and offers the potential for deep penetration and reduced heat-affected zones due to the narrow laser beam irradiation area.
- However, it is not suitable for filling gaps between components or for filler metal welding.
- *Subject to manual estimation by meviy Support
Spot Welding
- Two plates are clamped between electrodes and joined by applying a high voltage.
- It is suitable for thin plate processing and has the characteristic of being less prone to distortion after welding compared to arc welding.
Tip
- When reordering the same model number, welding will be performed using the same method as the initial order.
- This also applies when selecting the “Automatic (Arc or Laser)” welding type.
Welding Method
- The welding method can be set to continuous welding or intermittent welding. When intermittent welding is selected, the nominal welding length and the number of weld points can be set.
- The center-to-center distance between welds is automatically calculated for each welded edge based on the set welding length and the number of weld points per edge.

Continuous Welding
- Continuously welds areas without gaps.
- Effective for maintaining watertightness and airtightness at joints.
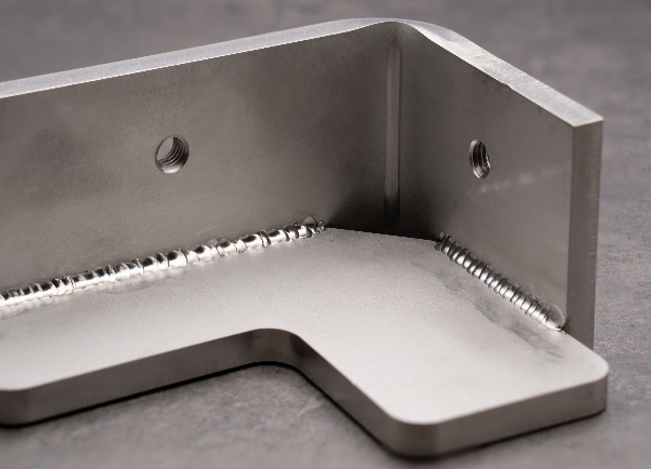
Intermittent Welding
- Welds areas at regular intervals.
- The weld length per side and the number of weld points can be specified.
- Reducing the weld length minimizes thermal distortion caused by welding.

Tip
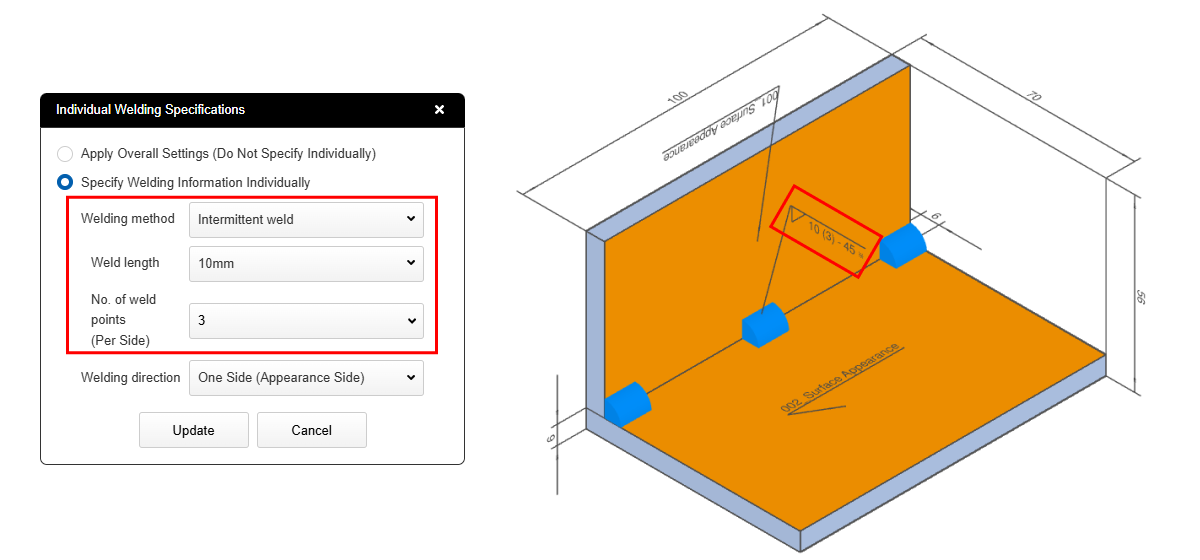
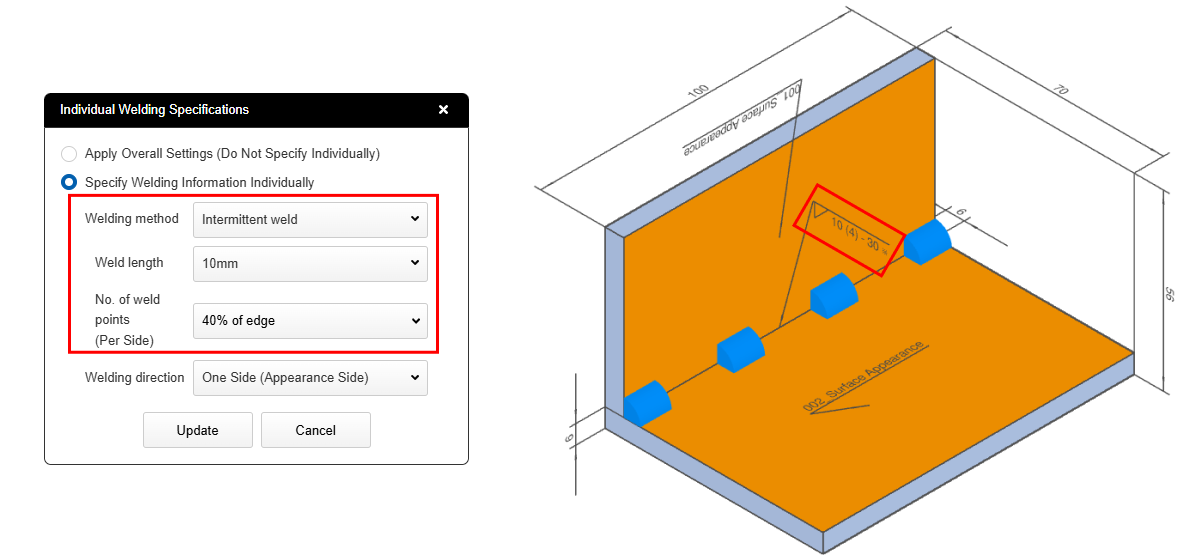
You can choose between two methods for specifying the number of weld locations: a fixed value or calculation based on a ratio.
-
Fixed value →For each edge, the weld spacing will be adjusted so that the specified number of welds (based on the fixed value) is applied.Example: For a weld length of 40 mm, with the settings “Weld Length: 10 mm” and “Number of Weld Locations (per edge): 3”
-
Ratio-Based Calculation →For each edge, the number of welds and weld spacing are adjusted so that the selected percentage of the edge is welded.Example: For a weld length of 40 mm, with the settings “Weld Length: 5 mm” and “Number of Weld Locations (per edge): 40%”
Caution
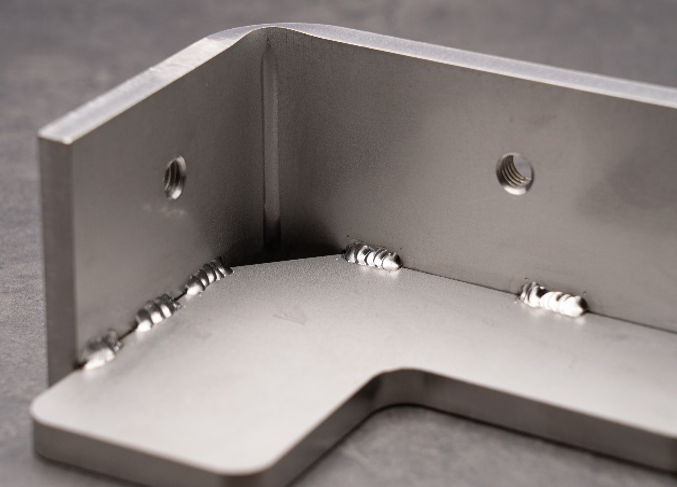
If the selected weld length and number of weld locations for intermittent welding exceed the available weldable edge length, the system will classify that section as continuous welding.
*Note: Intermittent welding cannot be applied when the spacing between welds is less than 5 mm.
Weld length: 30mm, Number of weld locations: 4
→ 30mm × 4 = 120mm which exceeds the weldable edge length of 100 mm, therefore it will be treated as continuous welding.
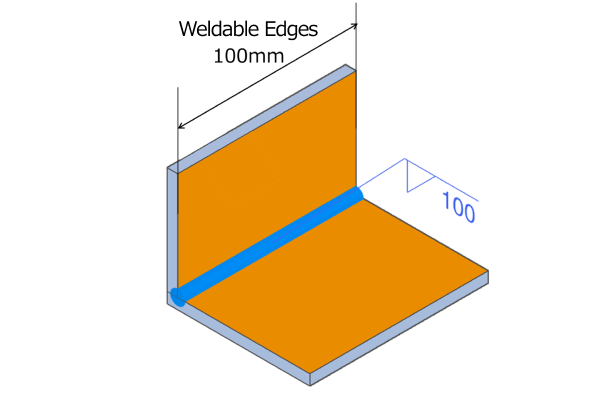 Example of a Case Treated as Continuous Welding
Example of a Case Treated as Continuous Welding
Welding direction
- The welding direction can be selected from the plate side (face side), the plate side (non-face side), or both sides.
- For T-welds between plate thickness surfaces and plate flat surfaces, or welds where plate flat surfaces overlap, the weld direction cannot be specified. In these cases, both sides are welded, or a full circumferential weld is performed excluding the bend section.
- The outer surface recognized by meviy is displayed in dark orange on the 3D viewer. By combining the part’s outer surface information with the welding direction setting, you can specify the desired welding location. For details, please refer to “Appearance Surface and Welding Direction Settings“.
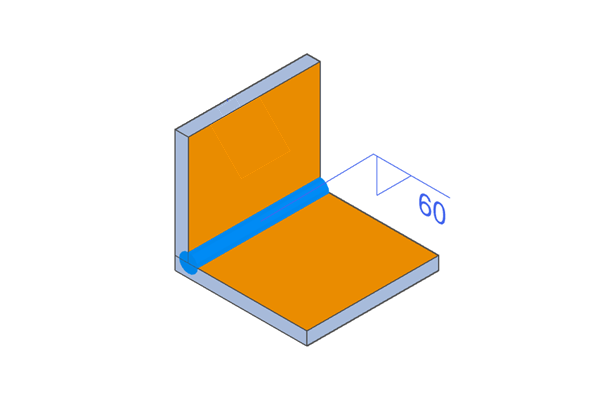
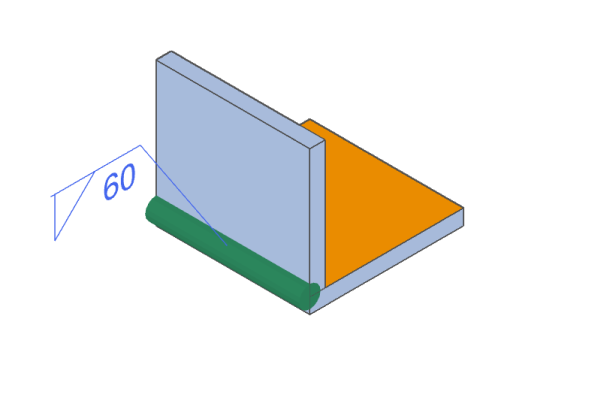
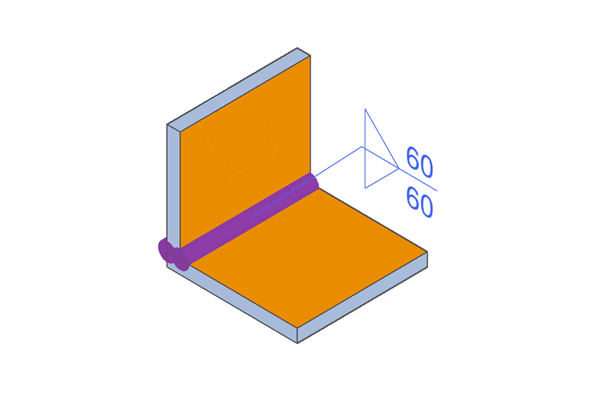
Surface-side (Face-side) Welding
Weld only the plate side (face side) of the plate to be welded.
One-side (non-face side) welding
Only the edge side (non-face side) of the plate to be welded is welded.
Double-sided welding
Both the visible side and the non-visible side are welded.
Caution
For T-welds between plate thick surfaces and plate flat surfaces, and welded joints where plate flat surfaces overlap cannot be specified for the welding direction.
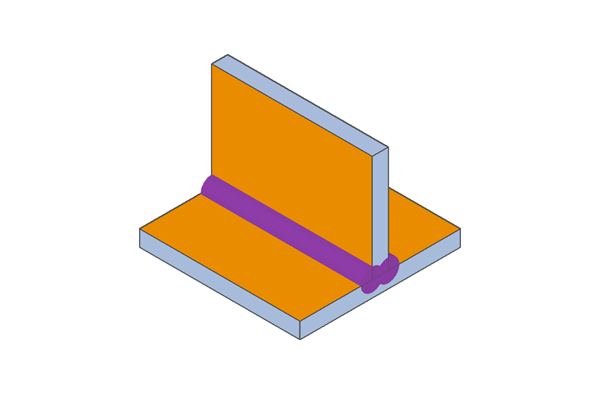 Example of T-welded flat plate surfaces
Example of T-welded flat plate surfaces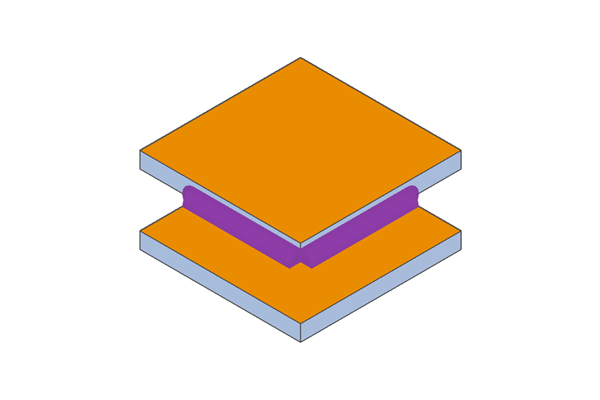 Example of T-weld on flat plate
Example of T-weld on flat plate
The processing direction for spot welding is determined during manufacturing based on the shape.
If you require spot welding from a specific orientation, please specify this in the additional instructions field and request a quote from our representative.
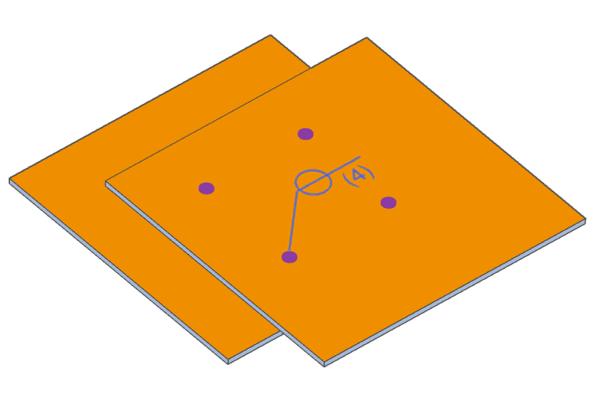
Examples of spot welding
Welding finish
- Weld finishing options include Burn Mark Removal only, grinder finishing, or other specifications listed in the Additional Instructions field.
- If you select “Other Additional Instructions,” please specify your desired welding finish in the “Other Additional Instructions” field and request a quote from the meviy Support.
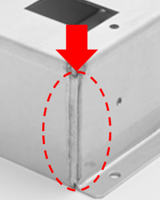

Burn Mark Removal Only
- This process removes heat-affected zones generated during welding.
- The descaling method is specified based on material and surface treatment.
- Depending on the material and surface treatment, weld discoloration may remain in areas where tools cannot reach.
Grinder finishing
- In addition to removing heat-affected zones caused by welding, the weld bead is ground away to achieve a finish that is flush with the surrounding surface.
- The grinding targets the product’s outer contour areas; weld beads in areas where tools cannot reach are not ground.
Other Additional Instructions
If you require finishing work not included in burnishing or grinding, please use the Manual Quote.
Example: Hairline finish on welded surfaces, oil bath to prevent water leakage, etc.
Please refer to the “Finish Processing Standards” for the finish condition for each material.
Caution
- The presence and method of spot welding finishing are determined by the material.
- For the finish condition for each material, please refer to the “Spot Welding and Finishing“.